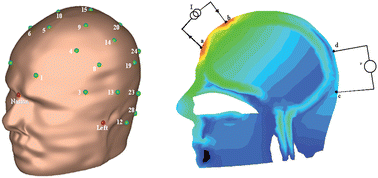
An analytical platform that imposes controlled mechanical strain onto live cells whilst monitoring changes in cell morphology and molecular signalling has been developed by scientists in Germany. Cellular processes induced by mechanical forces are crucial for bone healing and lung function. Understanding these processes could help to prevent and aid the development of therapies for mechanically induced lung and cardiovascular diseases and injuries.
Christine Kranz and colleagues from the University of Ulm combined fluorescence microscopy with atomic force microscopy to analyse the cells. They integrated a motorised cell stretching device into the system. ‘We combined the stretching device with biosensor technology, enabling localised measurements of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), for example, which is among the most important signalling molecule associated with mechanical stress,’ says Kranz. ‘Consequently, detecting ATP at the surface of mechanically stimulated cells facilitates investigation of the signalling cascades involved.’

The assembly includes a cell-stretching device, an atomic force microscopy head and an objective of the inverted microscope
To read the full article please visit Chemistry World.
Combining atomic force-fluorescence microscopy with a stretching device for analyzing mechanotransduction processes in living cells
E. Hecht , P. Knittel , E. Felder , P. Dietl , B. Mizaikoff and C. Kranz
Analyst, 2012, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C2AN36001B