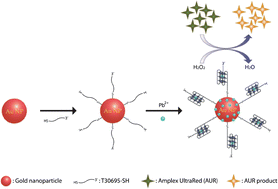
Lead has no biological function in the human body, and high concentrations can cause detrimental health effects, especially for children. The large instruments used for detecting lead mostly test contaminated water, and cannot be transported to remote areas or test blood samples. Huan-Tsung Chang and researchers at National Taiwan University created a unique binding complex composed of gold nanoparticles, DNA, and Amplex UltraRed to combat this problem. In this system, lead ions form an alloy with the gold nanoparticles increasing catalytic activity, which results in oxidation of the DNA-conjugated Amplex UltraRed and production of a detectable fluorescent signal. This simple yet effective sensor detected lead concentrations down to 0.1 nM in blood samples.
This paper will be free to read until the end of the month.
Peroxidase mimicking DNA–gold nanoparticles for fluorescence detection of the lead ions in blood
Chi-Lin Li, Chih-Ching Huang, Wei-Hsi Chen, Cheng-Kang Chiang and Huan-Tsung Chang
Analyst, 2012, 137, 5222-5228
DOI: 10.1039/C2AN35599J