Front cover: Konorov et al., Analyst, 2012, 137, 4662-4668
The latest issue of Analyst is online, with three cover articles for you to enjoy.
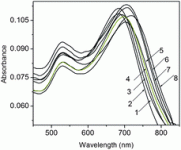
Our stunning front cover comes from the groups of Professor Robin Turner and Professor Michael Blades at the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada. Their study establishes the utility of Raman spectroscopy to non-invasively detect biologically relevant changes in live cells exposed to conditions known to trigger autophagy.
The centre image is a differential interference contrast image of two MCF-7 cells, a human breast cancer cell line, after being starved of glutamine for two days.
The surrounding four images are chemical maps based on Raman microspectroscopy of the same two cells rendered from chemically-selective band intensities that indicate the spatial distributions of DNA and RNA (upper-left); RNA only (upper-right); phospholipid (lower-left) mapped relative to nucleic acid; and hydroxyapatite (lower-right), which is a common marker for breast cancers and strongly associated with malignancy.
In each image, the red intensity indicates the highest concentration, blue the lowest. The advantage of this type of chemical imaging, according to the authors, is that it is non-destructive and label-free.
Raman microspectroscopy of live cells under autophagy-inducing conditions
Stanislav O. Konorov, Mario A. Jardon, James M. Piret, Michael W. Blades and Robin F. B. Turner
Analyst , 2012, 137, 4662-4668
DOI: 10.1039/C2AN35477B
Inside front cover, Salter et al., Analyst, 2012, 137, 4669-4676
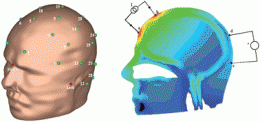
On the inside front cover, Dr Michael Hippler and colleagues from Sheffield University, UK, introduce a variant of cavity-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (CERS) in which diode laser radiation at 635 nm is coupled into an external linear optical cavity composed of two highly reflective mirrors. Using optical feedback stabilisation, build-up of circulating laser power by three orders of magnitude occurs. Strong Raman signals are collected in forward scattering geometry.
The authors say CERS has the potential to become a new standard method to monitor Raman active species, in particular important homonuclear gases like nitrogen, oxygen or hydrogen that can not be easily detected by alternative spectroscopic techniques.
Cavity-enhanced Raman spectroscopy with optical feedback cw diode lasers for gas phase analysis and spectroscopy
Robert Salter, Johnny Chu and Michael Hippler
Analyst , 2012, 137, 4669-4676
DOI: 10.1039/C2AN35722D
The image on the back cover is from Mridul Kanti Mandal and Kenzo Hiraoka of University of Yamanashi, Chuo, Japan, and their co-workers. They have developed a method to perform remote and direct sampling for mass spectrometry.
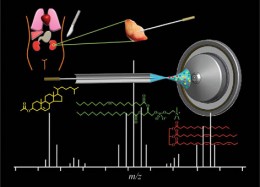
Back cover: Mandal et al., Analyst, 2012, 137, 4658-4661
They say that the method is easy to operate and versatile allowing any biological specimen to be sampled away from the instrument in a minimally invasive manner.
Solid probe assisted nanoelectrospray ionization mass spectrometry for biological tissue diagnostics
Mridul Kanti Mandal, Kentaro Yoshimura, Subhrakanti Saha, Satoshi Ninomiya, Md. Obaidur Rahman, Zhan Yu, Lee Chuin Chen, Yasuo Shida, Sen Takeda, Hiroshi Nonami and Kenzo Hiraoka
Analyst , 2012, 137, 4658-4661
DOI: 10.1039/C2AN36006C
All these cover articles will be free to access until the end of October, and don’t forget to also take a look at this issue’s HOT articles.