The latest issue of Analyst is now available for you to browse, and we head east for all three covers.
There’s nanoparticle-assisted laser desorption/ionisation MS from Japan, electrochemical biosensing from Korea, and microextraction from Taiwan.
On the front cover is work from Shu Taira of the School of Material Science at the Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST), Ishikawa, Japan, and colleagues.
They analysed oligonucleotides by nanoparticle-assisted laser desorption/ionization (nano-PALDI) mass spectrometry, and demonstrated that iron-based nanoparticles may serve as the assisting material of ionization for genes and other biomolecules.
Communication: Oligonucleotide analysis by nanoparticle-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry
Shu Taira, Issey Osaka, Shuich Shimma, Daisaku Kaneko, Tomoyuki Hiroki, Yasuko Kawamura-Konishi and Yuko Ichiyanagi
Analyst, 2012, 137, 2006-2010
DOI: 10.1039/C2AN16237G
The inside front cover features a HOT paper from Hye Jin Lee of Kyungpook National University, Daegu-city, Republic of Korea and her collaborators from Korea and the UK.
A novel electrochemical detection methodology is described for the femtomolar detection of proteins which utilizes both DNA aptamer-functionalized nanoparticles and a surface enzymatic reaction. The authors say this offers a significant improvement compared to conventional electrochemical-based immunoassay approaches and provides a foundation for the practical use and incorporation ofnanoparticle-enhanced detection into electrochemical biosensing technologies. This Communication is part of our web theme on Future Electroanalytical Developments.
Communication: Highly sensitive electrochemical detection of proteins using aptamer-coated gold nanoparticles and surface enzyme reactions
Eun Ji Nam, Eum Ji Kim, Alastair W. Wark, Sangchul Rho, Hyungi Kim and Hye Jin Lee
Analyst, 2012, 137, 2011-2016
DOI: 10.1039/C2AN15994E
Finally, the back cover highlights research from Shang-Da Huang of National Tsing Hua University, Hsinchu, Taiwan and co-workers.
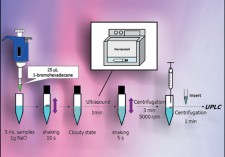
They have developed a rapid, simple equilibrium liquid-phase microextraction method based on manual shaking-enhanced, ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction (MS-USAEME) and measurement by UPLC-UV for the determination of five endocrine-disrupting phenols in seawater samples and in detergent samples.
Determination of endocrine-disrupting phenols in water samples by a new manual shaking-enhanced, ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction method
Ming-Wei Shu, Mei-I Leong, Ming-Ren Fuh and Shang-Da Huang
Analyst, 2012, 137, 2143-2150
DOI: 10.1039/C2AN16117F
These cover articles will be free to access for the next 5 weeks, and don’t forget to take a look at the collection of HOT articles featured in this issue too.