Perspective article – nanostructured carbon-based electrodes could be the answer…
The fast evolution of portable electronic devices and micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS) requires energy sources that have high power, high energy, long cycle life, and the adaptability to various substrates.
Two excellent candidates are lithium-ion batteries, which can store high energy on a gravimetric and volumetric basis but have relatively low power, and electrochemical capacitors (ECs) which are ideal for high power applications, but are limited for energy storage. There is now a need to develop materials with both high power and energy storage capabilities.
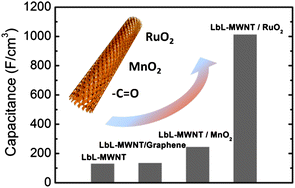
Currently, the excellent performance of nanostructured electrodes with thickness of a few microns can be integrated on Si chips or flexible plastic substrates, suggesting promising energy sources for portable electronic devices and micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS). If these nanostructured electrodes can be successfully scaled up to a thickness of hundreds of microns without losing performance, they could be promising for incorporation into electric vehicles, heavy machinery, and load-leveling applications.
Read the feature review today:
Nanostructured carbon-based electrodes: bridging the gap between thin-film lithium-ion batteries and electrochemical capacitors
Seung Woo Lee, Betar M. Gallant, Hye Ryung Byon, Paula T. Hammond and Yang Shao-Horn
Energy Environ. Sci., 2011, DOI: 10.1039/C0EE00642D