Top 25 most-read Nanoscale articles for Q2
Controlled assembly of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles on graphene oxide
Yi Zhang, Biao Chen, Liming Zhang, Jie Huang, Fenghua Chen, Zupei Yang, Jianlin Yao and Zhijun Zhang
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00776E
Controlled assembly of plasmonic colloidal nanoparticle clusters
José M. Romo-Herrera, Ramón A. Alvarez-Puebla and Luis M. Liz-Marzán
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00804D
The role of nanomaterials in redox-based supercapacitors for next generation energy storage devices
Xin Zhao, Beatriz Mendoza Sánchez, Peter J. Dobson and Patrick S. Grant
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00594K
Conjugated polymers/semiconductor nanocrystals hybrid materials—preparation, electrical transport properties and applications
Peter Reiss, Elsa Couderc, Julia De Girolamo and Adam Pron
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00403K
Fabrication of carbon nanofiber–polyaniline composite flexible paper for supercapacitor
Xingbin Yan, Zhixin Tai, Jiangtao Chen and Qunji Xue
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00470G
Luminescent nanomaterials
Claus Feldmann
DOI: 10.1039/C1NR90008K
Graphene edges: a review of their fabrication and characterization
Xiaoting Jia, Jessica Campos-Delgado, Mauricio Terrones, Vincent Meunier and Mildred S. Dresselhaus
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00600A
A multiscale simulation study of carbon nanotube interactions with designed amphiphilic peptide helices
E. Jayne Wallace, Robert S. G. D’Rozario, Beatriz Mendoza Sanchez and Mark S. P. Sansom
DOI: 10.1039/B9NR00355J
Preparation of functional magnetic nanocomposites and hybrid materials: recent progress and future directions
Silke Behrens
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00634C
Surfactant-assisted, shape-controlled synthesis of gold nanocrystals
Junyan Xiao and Limin Qi
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00814A
Electrostatics at the nanoscale
David A. Walker, Bartlomiej Kowalczyk, Monica Olvera de la Cruz and Bartosz A. Grzybowski
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00698J
Facile synthesis of metal oxide/reduced graphene oxide hybrids with high lithium storage capacity and stable cyclability
Jixin Zhu, Ting Zhu, Xiaozhu Zhou, Yanyan Zhang, Xiong Wen Lou, Xiaodong Chen, Hua Zhang, Huey Hoon Hng and Qingyu Yan
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00744G
Graphene-wrapped TiO2 hollow structures with enhanced lithium storage capabilities
Jun Song Chen, Zhiyu Wang, Xiao Chen Dong, Peng Chen and Xiong Wen (David) Lou
DOI: 10.1039/C1NR10162E
Liquid-phase exfoliation, functionalization and applications of graphene
Xu Cui, Chenzhen Zhang, Rui Hao and Yanglong Hou
DOI: 10.1039/C1NR10127G
Current directions in core–shell nanoparticle design
Wolfgang Schärtl
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00028K
Mechanised nanoparticles for drug delivery
Karla K. Cotí, Matthew E. Belowich, Monty Liong, Michael W. Ambrogio, Yuen A. Lau, Hussam A. Khatib, Jeffrey I. Zink, Niveen M. Khashab and J. Fraser Stoddart
DOI: 10.1039/B9NR00162J
2D materials: to graphene and beyond
Rubén Mas-Ballesté, Cristina Gómez-Navarro, Julio Gómez-Herrero and Félix Zamora
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00323A
Fabrication of hybrids based on graphene and metal nanoparticles by in situ and self-assembled methods
Fu-An He, Jin-Tu Fan, Fei Song, Li-Ming Zhang and Helen Lai-Wa Chan
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00672F
Microwave chemistry for inorganic nanomaterials synthesis
Idalia Bilecka and Markus Niederberger
DOI: 10.1039/B9NR00377K
Semiconductor nanostructure-based photovoltaic solar cells
Genqiang Zhang, Scott Finefrock, Daxin Liang, Gautam G. Yadav, Haoran Yang, Haiyu Fang and Yue Wu
DOI: 10.1039/C1NR10152H
Solution synthesis of one-dimensional ZnO nanomaterials and their applications
Benjamin Weintraub, Zhengzhi Zhou, Yinhua Li and Yulin Deng
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00047G
TiO2nanotubes and their application in dye-sensitized solar cells
Poulomi Roy, Doohun Kim, Kiyoung Lee, Erdmann Spiecker and Patrik Schmuki
DOI: 10.1039/B9NR00131J
Small-sized silicon nanoparticles: new nanolights and nanocatalysts
Zhenhui Kang, Yang Liu and Shuit-Tong Lee
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00559B
Gold nanoparticles for the colorimetric and fluorescent detection of ions and small organic molecules
Dingbin Liu, Zhuo Wang and Xingyu Jiang
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00887G
Surface charge of gold nanoparticles mediates mechanism of toxicity
Nicole M. Schaeublin, Laura K. Braydich-Stolle, Amanda M. Schrand, John M. Miller, Jim Hutchison, John J. Schlager and Saber M. Hussain
DOI: 10.1039/C0NR00478B


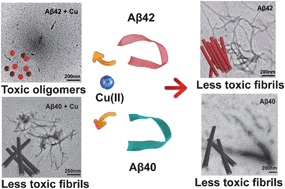








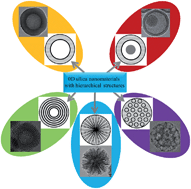
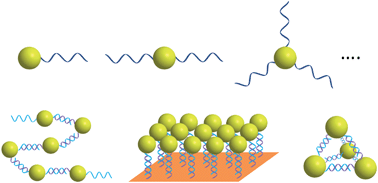



 Lifeng Yan and colleagues at the University of Science and Technology of China, Heifei, have prepared 3D graphene structures by self-assembly from graphene oxide using mild chemical reduction in water at 95 degrees Celsius at atmospheric pressure without stirring. The graphene shapes were controlled by using reactor vessels of differing shapes. The team were able to produce cylinder-, pear- and sphere-like shapes. ‘The process is quite simple – any macroscopic 3D graphene shapes can be prepared at room temperature and pressure,’ explains Yan.
Lifeng Yan and colleagues at the University of Science and Technology of China, Heifei, have prepared 3D graphene structures by self-assembly from graphene oxide using mild chemical reduction in water at 95 degrees Celsius at atmospheric pressure without stirring. The graphene shapes were controlled by using reactor vessels of differing shapes. The team were able to produce cylinder-, pear- and sphere-like shapes. ‘The process is quite simple – any macroscopic 3D graphene shapes can be prepared at room temperature and pressure,’ explains Yan.