As cancer treatments evolve, focus has shifted to techniques and tools, which provide tumor-targeting capabilities and are uncoupled from common detrimental side effects. The efficient delivery of new therapeutics has been a common area of interest, with studies focused on nanoparticle delivery systems being an eminent research area.
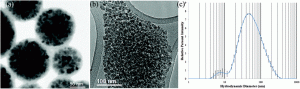
(a) TEM image of PS/Fe3O4 microspheres showing the amorphous coating entrapping multiple Fe3O4 nuclei. (b) TEM image of PAA/Fe3O4 and (c) cumulant size distribution of PAA/Fe3O4.
In this review article, Shi and co-workers draw attention to the properties of magnetite nanoparticles (Fe3O4), which can be utilised as customized therapeutics. This review provides an overview of the synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles with an in-depth discussion related to their synthesis, functionalization and applications in a biological environment.
A highlight of this review includes an exploration into the recently discovered photo-luminescence properties of magnetite nanoparticles through studies of the electronic band structures to explain the emission mechanisms occurring. The implications of thermal and magnetic induced hypothermia treatments utilizing these nanoparticles are also discussed relative to the patients being treated by such techniques.
From this review it can be determined that a new theragnostic platform has emerged with multi-functional capabilities both in terms of imaging and drug delivery.
Photo-fluorescent and magnetic properties of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications
Donglu Shi, M. E. Sadat, Andrew W. Dunn and David B. Mast
Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 8209-8232. DOI: 10.1039/C5NR01538C
Dr Derek Craig is a guest web writer for the Nanoscale blog. He is a Post Doctoral Research Fellow at the University of St. Andrews based in the fields of Biophotonics and Materials Science. With a background in chemistry, his work mainly focuses on the synthesis of nano to meso materials and the use of imaging techniques to study biological samples.