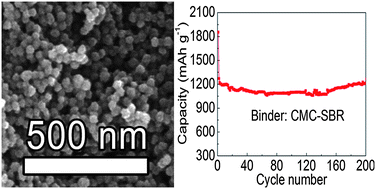
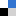Lixia Yuan, Yunhui Huang and co-workers report a simple one-pot method to synthesize a nanocluster composite assembled by interconnected ultrafine SnO2@C nanospheres in their recent Nanoscale paper. They found that with a mixture of sodium carboxyl methyl cellulose and styrene butadiene rubber as a binder, the SnO2@C nanocluster anode exhibits superior cycling stability and rate capability.
Electrode materials are crucial for the overall performance of lithium ion batteries. Graphite is a traditionally used anode material, and tin dioxide is one promising alternative with a higher theoretical lithium storage capacity. However, the practical use of tin dioxide is limited by its rapid capacity fading, low initial coulombic efficiency and poor rate performance. Scientists from China have recently come up with a clever solution to these problems by skilfully combining SnO2@C nanoclusters with a suitable binder.
Read this HOT article today:
A SnO2@carbon nanocluster anode material with superior cyclability and rate capability for lithium-ion batteries
Min He, Lixia Yuan, Xianluo Hu, Wuxing Zhang, Jie Shu and Yunhui Huang
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR34133J