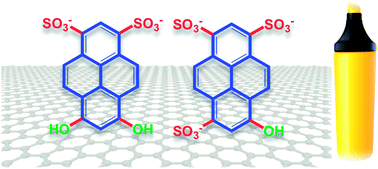
Scientists from Italy, the UK, Belgium and France provide insights into the efficiency of pyrene sulfonic sodium salts for the preparation of graphene in their recent Nanoscale paper, and clarify the role of different molecular properties on graphene exfoliation.
They compared pyrene derivatives with increasing number of sulfonic groups for their efficiency as exfoliating agents in the preparation of graphene. They combined different experimental and modelling techniques to find a correlation between the graphene-pyrene dye interaction, the molecular structure and the amount of graphene flakes solubilised. They found that a large dipole and molecular asymmetry are important for adsorption of the dye molecule on graphene. The dipole allows the molecule to “slide” into the solvent layer between the graphene surface and the aromatic core of the dye, and displace the water molecules.
The efficiency of pyrene derivatives in exfoliating graphene is well known, but the details of their interactions with graphene have been somewhat unclear so far. An understanding of these interactions is important for developing the processability of graphene, which holds great potential for technological applications in numerous fields.
Read this HOT article today:
Nanoscale insight into the exfoliation mechanism of graphene with organic dyes: effect of charge, dipole and molecular structure
Andrea Schlierf, Huafeng Yang, Elias Gebremedhn, Emanuele Treossi, Luca Ortolani, Liping Chen, Andrea Minoia, Vittorio Morandi, Paolo Samorì, Cinzia Casiraghi, David Beljonne and Vincenzo Palermo
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR00258F