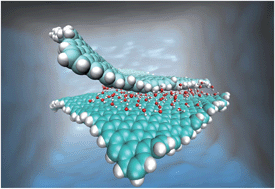
They found that the interfacial water monolayers hinder the aggregation of graphene nanosheets, attributed to the many structurally ordered H-bonds of the water monolayer. Their findings advance understanding of the hydrophobic assembly of nanomaterials, such as proteins in aqueous solution.
Read this Nanoscale paper in full:
The interfacial-organized monolayer water film (MWF) induced “two-step” aggregation of nanographene: both in stacking and sliding assembly pathways
Wenping Lv and Ren’an Wu
DOI: 10.1039/C3NR33447C