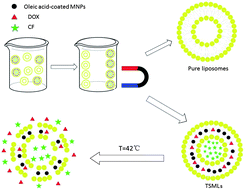
Researchers based at Chongqing University in China have reported the synthesis of thermosensitive magnetic liposomes which release 5-(and-6)-carboxylfluorescein and the cancer drug doxorubicin only when the temperature reaches 42 °C. The materials are stable at body temperature, but irradiation with infrared light allows drug release by causing a change in permeability of the liposome membrane.
The authors suggest that the system has great potential for the efficient release of both hydrophobic and hydrophilic drugs.
Read this HOT Communication in full:
Biocompatible magnetic liposomes for temperature triggered drug delivery
Xingwei Ding, Kaiyong Cai, Zhong Luo, Jinghua Li, Yan Hu and Xinkun Shen
Nanoscale, 2012, DOI: 10.1039/C2NR31292A