The emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) has has been a HOT topic in recent years due to their notorious implication in ozone layer depletion and the formation of ground level ozone. A specific type of VOC, Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) are also known to be carcinogenic. Catalytic oxidation has been utilised as one of the most effective ways to remove unwanted contaminants such as these, however, this usually involves expensive noble metals. In a move towards alternative materials such as metal-oxides, highly-active CeO2 has recently been applied to reactions such as the above, CO oxidation and soot combustion – however, their widespread uptake by industry has been restricted by their poor thermal stability.
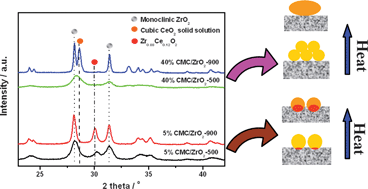
High thermal stability of ceria-based mixed oxide catalysts supported on zirconia for toluene combustion
Chen et al. have developed a simple, inexpensive and effective solution to the thermal stability problem, by loading mixed CeO2-based oxides on ZrO2. The catalytic combustion of toluene was studied and the ZrO2 carrier was shown to not only to stabilise the surface active structure of the catalyst but also to improve its efficiency by enhancing O2 mobility.
Read more about the potential of these catalysts by downloading the full article for FREE at:
High thermal stability of ceria-based mixed oxide catalysts supported on ZrO2 for toluene combustion
Han-Feng Lu, Ying Zhou, Wen-Feng Han, Hai-Feng Huang and Yin-Fei Chen
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2013, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C3CY20754D
You may also be interested in a related article:
High activity mesoporous copper doped cerium oxide catalysts for the total oxidation of polyaromatic hydrocarbon pollutants
Asunción Aranda, Elvira Aylón, Benjamín Solsona, Ramón Murillo, Ana María Mastral, David R. Sellick, Said Agouram, Tomás García and Stuart H. Taylor
Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 4704–4706
DOI: 10.1039/C2CC31206A
Comments Off on Catalysts losing their nobility
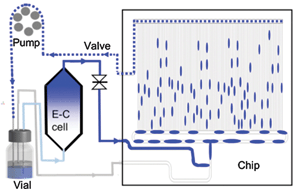 Many biocatalysts require expensive co-factors when they are used in the production of industrially relevant compounds, but a team of UK chemists has replaced one such co-factor – nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) – with a smaller, more practical molecule: methyl viologen.
Many biocatalysts require expensive co-factors when they are used in the production of industrially relevant compounds, but a team of UK chemists has replaced one such co-factor – nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) – with a smaller, more practical molecule: methyl viologen.