Hoon Suk Rho1, Yoonsun Yang2, Henk-Willem Veltkamp1, and Han Gardeniers1
1Mesoscale Chemical Systems Group, MESA+ Institute for Nanotechnology, University of Twente, The Netherlands.
2Medical Cell BioPhysics Group, MIRA Institute for Biomedical Technology and Technical Medicine, University of Twente, The Netherlands.
Why is this useful?
Most common way to handle and transport reagents in chemical or biological labs is by using a pipette. However, tubing connection is generally used for the delivery of reagents into a microfluidic device. Even though the connection with commercial tubing and connectors allows various choices on the sizes and materials of the tubing and easy connection, difficult sampling from stock solutions, dead volume in tubing and connectors, and extra sterilization on tubing and connectors for biomaterials, still remain challenges. Here we demonstrate a direct connection of pipette tips to a PDMS device and loading reagents by pressure driven flow.
What do I need?
- Stainless still puncher (Syneo LLC)
- Precision stainless steel tip (23 gauge, #7018302, Nordson Corporation)
- Tygon tubing (0.020″ x 0.060″OD, #EW-06418-02, Cole-Parmer Instrument Company)
- 3D printed plug
- Pliers
What do I do?
Punching inlet and outlet on a PDMS device
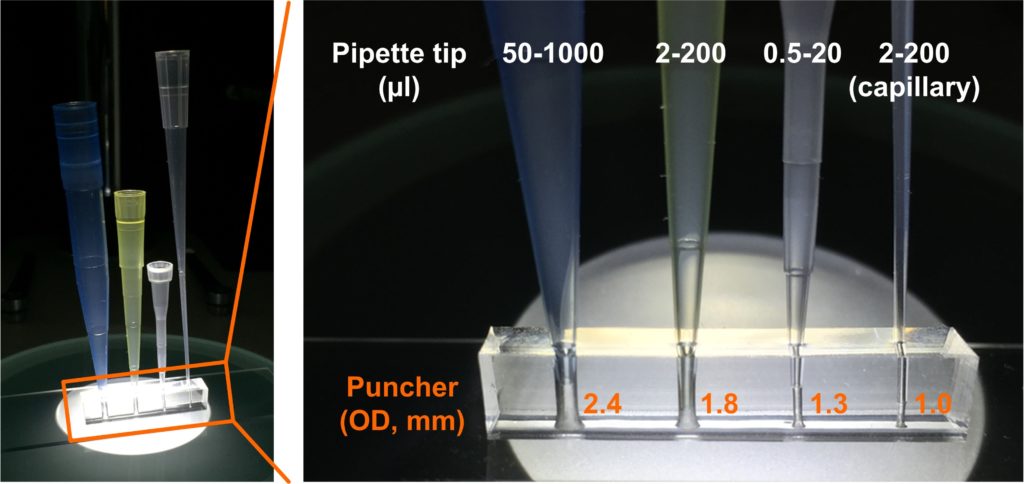
1. Select the size of a puncher based on the size of a pipette tip will be connected. We achieved tight connections of pipette tips on a PDMS substrate when we punched holes by using punchers with outer diameter of 2.4 mm, 1.8 mm, 1.3 mm, and 1.0 mm for 50 – 1000 µl, 2 – 200 µl, 0.5 – 20 µl, and 2 – 200 µl (capillary) pipette tips, respectively.
Plug connection preparation
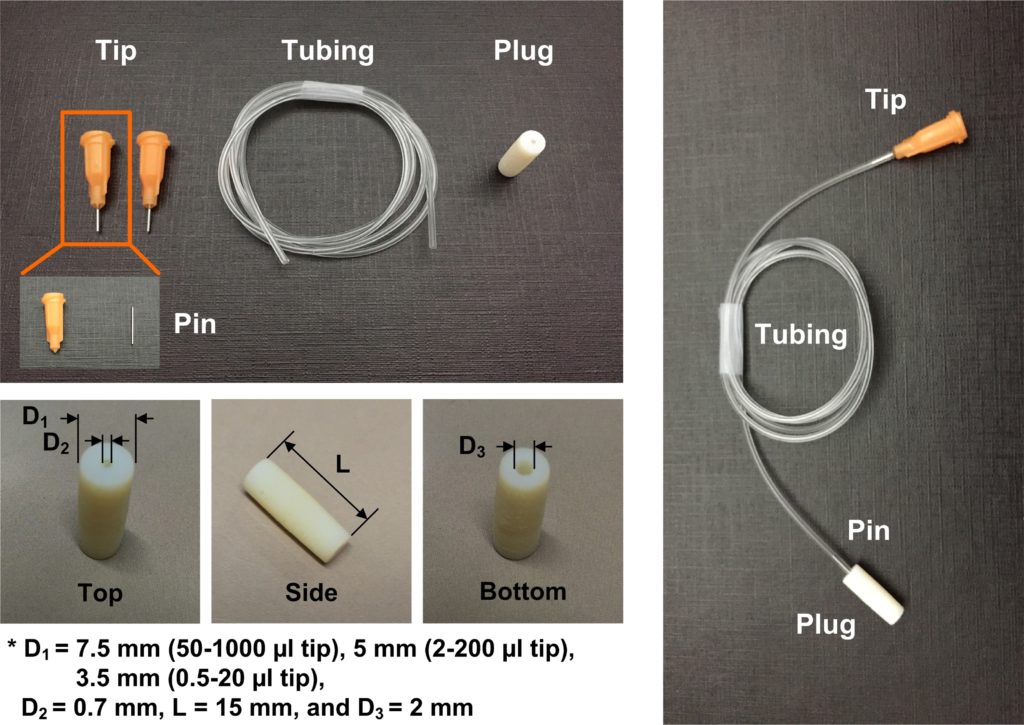
1. Separate a pin from a precision stainless steel tip. The pin can be easily removed by twisting the plastic part while the pin is held by pliers.
2. 3D-print a plug. The outer diameter of the plug depends on the size of the pipette tip that will be connected. The detailed dimensions of the plug are shown in Fig. 2.
3. Connect a precision stainless steel tip, tubing, a pin, and a plug. Because the plastic part of the tip is luer tapped, it can be connected to male luer connectors and commercial plastic syringes.
Solution loading
1. Pipette the sample, connect the pipette tip into the inlet of a PDMS device, and take off the pipette. When an empty pipette tip is connected into the outlet of the device, the sample from the outlet can be collected in the tip.
2. Insert the plug into the tip and connect the tip to a pressure source. When pressure is applied into the pipette tip, the solution in the tip is pushed into a microchannel (Fig. 3A). The luer tip can be connected to a syringe and a syringe pump can be used as a pressure source (Fig. 3B). The flow rate of the sample solution can be controlled by the syringe pump. The luer tip also can be connected to a pressure regulator with a luer fitting. Fig. 3C shows the flow rate of sample loading at various applied pressures controlled by a pressure regulator. In this case an external gas source is required. However, this system is cheaper than commercial microfluidic flow control systems. Also a digital pressure regulator can be used for accurate flow rate control at the low flow rate regime less than 1 µl/min.
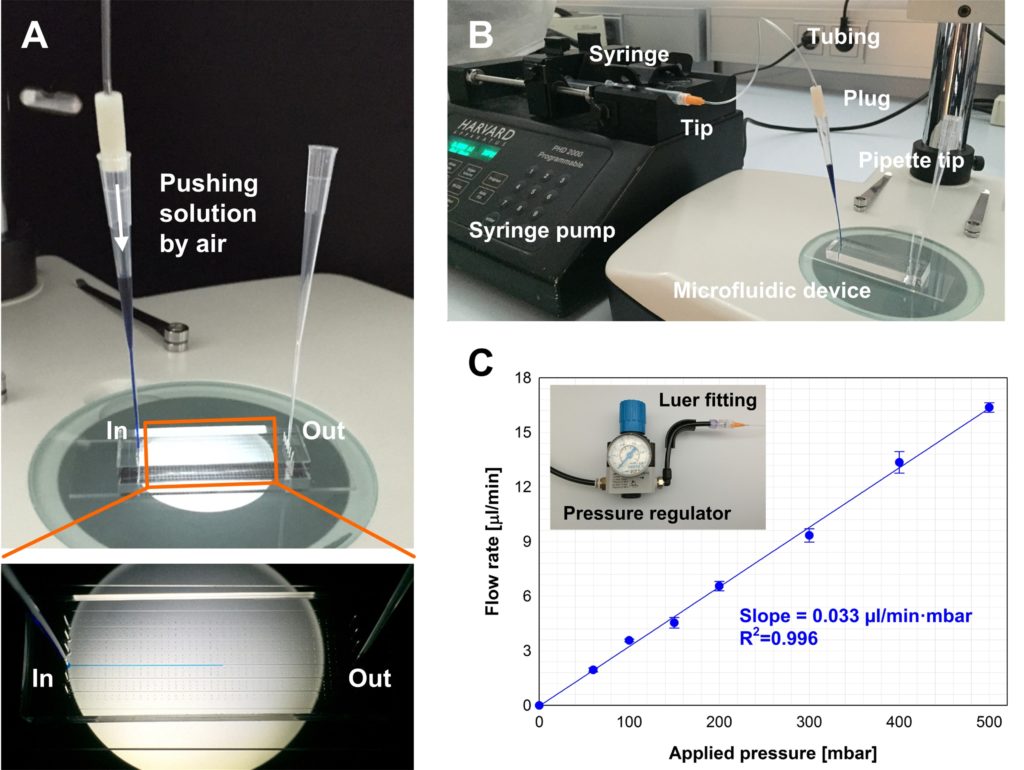
Fig. 3 A. Loading blue food dye solution into a microchannel, B. Solution loading by a syringe pump, and C. Solution loading by using a pressure regulator.
What else should I know?
No leakage of the solution was observed in the connection of a pipette tip onto a 1mm thick PDMS substrate. However at least a thickness of 3 mm is highly recommended to achieve tight fitting and stable support for the pipette tip. The pin obtained from a precision stainless tip is very useful for tubing connections. For example two separated tubes can be connected by the pin and also the pin can be inserted into an inlet or outlet of a PDMS device punched by a puncher with an outer diameter of 1mm. Also the pin can be easily bent by using pliers for compact connection to a PDMS device.