About this article:
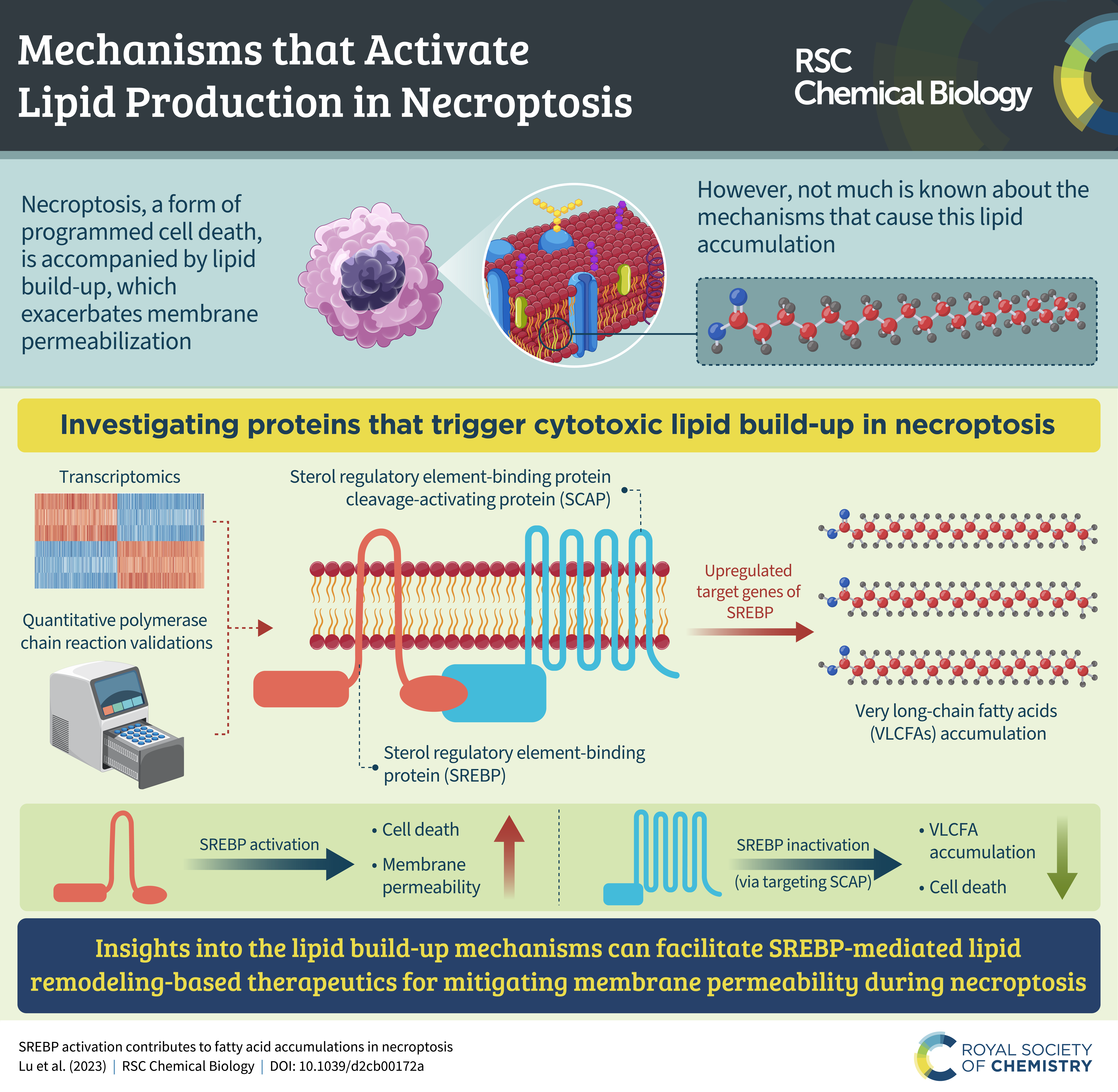
Necroptosis is a type of programmed cell death that is accompanied by extensive inflammatory activity. Previously, it has been shown that lipids accumulate in this process, and the accumulation exacerbates the membrane permeability and cell death in necroptosis.
However, the mechanisms that result in the accumulation of these lipids are unknown.
In this work, the authors used a global transcriptomics approach. They investigated the changes in the expression of proteins involved in lipid biosynthesis and transport to identify upstream mechanisms that cause lipid accumulation in necroptosis. Such a transcriptomics approach combined with further targeted experiments revealed the activation of a key regulatory mechanism of lipid production, namely sterol regulatory element binding proteins.
The authors showed that modulating the activation of sterol regulatory element binding proteins impacts necroptotic phenotype, demonstrating the functional role of these proteins in the accumulation of toxic lipids in necroptosis. Moreover, these results provide insights into mechanisms that regulate lipid production in cell death.
About RSC Chemical Biology
Led by Hiroaki Suga (University of Tokyo), RSC Chemical Biology is dedicated to publishing and disseminating the most exceptionally significant, breakthrough findings of interest to the chemical biology community. All submissions are handled by our experienced and internationally recognised Associate Editors. For more information on the journal, please visit the journal homepage.
As a gold open access journal, there are no barriers to accessing content and your research article will reach an international audience. Please note that the article processing charges are waived until mid-2022, so the journal is currently free to publish in.
RSC Chemical Biology is now indexed in the Directory of Open Access Journals (DOAJ), PubMed Central, Scopus and Web of Science: Emerging Sources Citation Index. Find out more about the journal and submit your work at rsc.li/rsc-chembio
Royal Society of Chemistry


