After tragic events like the devastating arsenic poisoning in Bangladesh in 2010, the exposure of drinking water to arsenic is a very serious concern worldwide.
Past studies have shown that removal of arsenic by nanoparticles in the presence of Humic Acid (HA) has a negative role. Now, for the first time, Blain Paul and colleagues have reported a positive influence of HA on graphene–Fe3O4 nano-composites for the removal of arsenic in water.
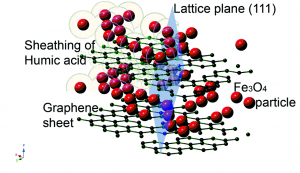
Contradictory to the general belief that HA has a negative effect on the ability of any system to absorb arsenic from water, this remarkable study demonstrates a role reversal of HA where it actually enhances the ability of graphene-Fe3O4 nano-composite to remove arsenic from ground water.
Researchers from the University of Johannesburg assembled Fe3O4 nanoparticles on graphene oxide sheets and coated with humic acid. The humic acid coating not only enhanced the nano-composites absorption ability, but almost doubled the removal efficiency of As(III) and As(V), opening a new dimension in the practical utilisation of nanotechnology in water research for arsenic removal.
Download the full paper for free* to find out how humic acid coating could significantly alter mechanism through π–π interactions, positively enhancing the removal of arsenic from water:
Graphene in the Fe3O4 nano-composite switching the negative influence of humic acid coating into an enhancing effect in the removal of arsenic from water
Blain Paul, Vyom Parashara and Ajay Mishra
Environ. Sci.: Water Res. Technol., 2015, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/ C4EW00034J
*Access is free through a registered RSC account – click here to register