From the Haber process to discrete enzymatic reactions iron is an important element in catalytic chemistry. Up until recently, however, iron has been significantly under-utilised as a homogeneous catalyst in organic synthesis compared to other transition metals. Recently homogeneous iron-based catalysts have undergone much development with some notable breakthroughs. Muftah Darwish and Martin Wills have compiled a thorough review of these in their HOT Perspective “Asymmetric catalysis using iron complexes – ‘Ruthenium Lite’?”. If you’re looking to reduce ketones or imines, perform transfer hydrogenation or asymmetric hydrosilylation this review will bring you up to date on the latest and greatest capabilities of these advanced iron complexes.
Read the full article for free in Catalysis Science & Technology.
Asymmetric catalysis using iron complexes – ‘Ruthenium Lite’?
Muftah Darwish and Martin Wills
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2012, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C1CY00390A, Perspective








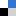






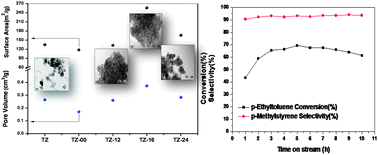 In this Catalysis Science and Technology HOT Article, the selective synthesis of an amorphous titania-zirconia mixed oxide with a very high specific surface area is described. The synthesized mixed oxide has been thoroughly characterized by various techniques and evaluated for an important oxidative dehrogenation reaction using CO2 as a soft oxidant.
In this Catalysis Science and Technology HOT Article, the selective synthesis of an amorphous titania-zirconia mixed oxide with a very high specific surface area is described. The synthesized mixed oxide has been thoroughly characterized by various techniques and evaluated for an important oxidative dehrogenation reaction using CO2 as a soft oxidant.
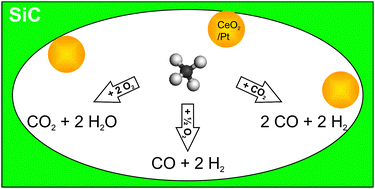 Stefan Kaskel and team look at the partial oxidation and dry reformation of methane using a ceria/platinum catalyst on a silicon carbide support in this Catalysis Science & Technology Hot article.
Stefan Kaskel and team look at the partial oxidation and dry reformation of methane using a ceria/platinum catalyst on a silicon carbide support in this Catalysis Science & Technology Hot article.
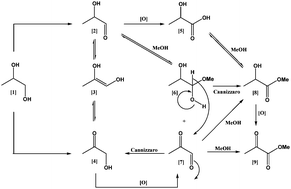 In this HOT article, the efforts of Graham Hutchings and co-workers to produce efficient catalysts based on gold and gold palladium nanoparticles supported on a variety of supports for the clean transformation of 1,2-propanediol (important in the synthesis of fine chemicals) to methyl lactate and methyl pyruvate are described.
In this HOT article, the efforts of Graham Hutchings and co-workers to produce efficient catalysts based on gold and gold palladium nanoparticles supported on a variety of supports for the clean transformation of 1,2-propanediol (important in the synthesis of fine chemicals) to methyl lactate and methyl pyruvate are described.