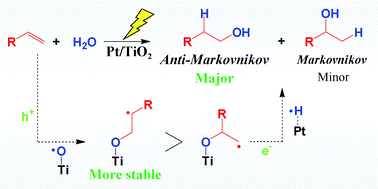
Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) to date presents the most promising deNOx technology for diesel engines. Removal of NOx from diesel exhaust is problematic due to the wide temperature range (373–923 K) at which diesel engines operate. This is due to inefficient conversion at low temperature (below 423 K) with the commonly used ionic exchanged zeolites or low selectivity to N2 with supported MnOx catalysts.
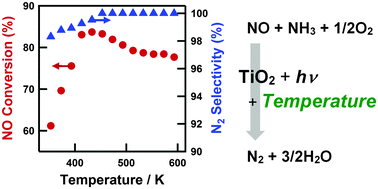
- In this HOT article, Tanaka et al. found that the temperature had a significant effect on the photocatalytic reactions in the gas phase over a TiO2 photocatalyst with a maximum conversion of 84% (at GHSV 100,000 h-1 and 433 K). The amount of NH3 at high temperature was found to be key to a high NO conversion. The results provide evidence of the potential practicality of the use of photo-SCR for diesel engines.
Effects of reaction temperature on photocatalytic activity
Read more about these developments in photocatalysis by downloading the article now:
Effects of reaction temperature on the photocatalytic activity of photo-SCR of NO with NH3 over a TiO2 photocatalyst
Akira Yamamoto, Yuto Mizuno, Kentaro Teramura, Tetsuya Shishido and Tsunehiro Tanaka
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2013, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C3CY00022B
This article is part of a themed issue on photocatalysis that is due to be published later this year.
You may also be interested in a perspective recently published by the same author on the subject:
A unique photo-activation mechanism by “in situ doping” for photo-assisted selective NO reduction with ammonia over TiO2 and photooxidation of alcohols over Nb2O5
Tetsuya Shishido, Kentaro Teramura and Tsunehiro Tanaka
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2011, 1, 541-551
DOI: 10.1039/C1CY00104C, Perspective