Carbon dioxide is one of the major contributors to global climate change and there are mounting concerns over the emission of such greenhouse gases. Research into the reduction of CO2 emissions is widespread. The development of technologies to generate renewable energies is the most desirable way in the long term.
Carbon dioxide is one of the major contributors to global climate change and there are mounting concerns over the emission of such greenhouse gases. Research into the reduction of CO2 emissions is widespread. The development of technologies to generate renewable energies is the most desirable way in the long term.
However, at present, these technologies are not able to replace existing fossil fuel-based power generation. Recent innovations have made the photocatalysis technology a potentially promising alternative.
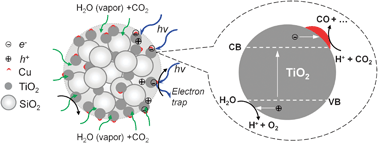
Now, in this Catalysis Science & Technology Hot Article, Pratim Biswas et al., from Washington University in St. Louis, USA describe, for the first time, the rapid and direct synthesis of nanostructured copper-doped titania–silica (Cu–TiO2–SiO2) composite particles for CO2 photoreduction using a furnace aerosol reactor (FuAR). This method is both simple and effective, with an extremely short processing time ( several seconds).
Read the article for free here.
Rapid synthesis of nanostructured Cu–TiO2–SiO2 composites for CO2 photoreduction by evaporation driven self-assembly
Wei-Ning Wang, Jinho Park and Pratim Biswas
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2011, Advance Article, DOI: 10.1039/C0CY00091D