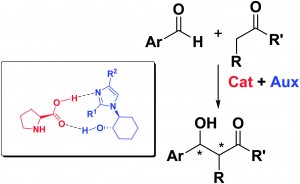
(L)-proline is a common organocatalyst used in synthetic reactions to produce chiral molecules as it is cheap and readily available. However, it is not very efficient, and there has been much interest in optimising its performance. One method is the modification of (L)-proline through a redesign and resynthesis, which can be quite complex. An easier alternative is to find additives that can improve the reaction in terms of yield and selectivity.
In this paper, the authors synthesised and investigated the effects of a chiral additive, enantiopure substituted imidazoles, on the (L)-proline-catalyzed aldol reaction. They found that it has greatly improved the selectivity of the reaction and the reaction rate. Addition studies of the reaction mechanism suggests that the supramolecular complex formed by the imidazole and (L)-proline helps to improve the efficiency of the catalyst. Further work on different co-catalysts can open up many more reactions in which (L)-proline can be used as an effective catalyst.
Read the paper and find out more.
Chemoenzymatic synthesis of optically active 2-(2′- or 4′-substituted-1H-imidazol-1-yl)cycloalkanols: chiral additives for (L)-proline
Raul Porcar, Nicolás Ríos-Lombardía, Eduardo Busto, Vicente Gotor-Fernández, Vicente Gotor, Eduardo Garcia-Verdugo, M. Isabel Burguete and Santiago V. Luis
Catal. Sci. Technol., 2013, Advance Article
DOI: 10.1039/C3CY00107E, Paper