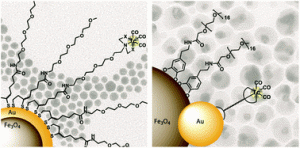
Bi-modal imaging agents are becoming more popular as they can be used to overcome limitations of single imaging modalities. In this work, radiolabelling of gold containing magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4-Au) with a nuclear isomer of technetium (99mTc), a commonly used radionuclide for clinical photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), was assessed using two different methods. In the first approach, Fe3O4-Au core-shell nanoparticles were coated with ligands containing thiol groups to bind to gold and chelator groups for [99mTc(CO)3]+. In the second approach, 99mTc containing ligands were first synthesised, then attached to gold on Fe3O4-Au dumbbell-like nanoparticles. Both synthetic routes were successful in providing a sufficient radiochemical yield on the surface of magnetic nanoparticles, and are ideal candidates as dual magnetic resonance imaging MRI/SPECT imaging agents. In future studies, the authors plan to use the radiolabelled magnetic particles for bimodal imaging of tumours, through attachment of cancer-specific targeting vectors.
99mTc radiolabelling of Fe3O4–Au core–shell and Au–Fe3O4 dumbbell-like nanoparticles
M. Felber and R. Alberto
Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 6653-6660. DOI: 10.1039/C5NR00269A
Dr Mike Barrow is a guest web writer for the Nanoscale blog. He currently works as a Postdoctoral Researcher at the University of Liverpool.