We are very pleased to introduce Juan A. Allegretto and Matías Rafti, authors of the paper ‘Synthesis and characterization of thermoresponsive ZIF-8@PNIPAm-co-MAA microgel composites with enhanced performance as an adsorption/release platform‘. Their article has been very well received and handpicked by our reviewers and handling editors as one of our HOT articles. Matías was kind enough to tell us more about the work that went into this article and what they hope to achieve in the future. You can find out more about the authors and their article below and find more HOT articles in our online collection.
Meet the Authors

Juan A. Allegretto holds a Chemistry BSc from the National University of La Plata (Universidad Nacional de La Plata – 2016), and currently conducts a PhD project related to MOFs synthesis and integration into diverse composites at the Universidad de San Martin, Argentina under the supervision of Professor Omar Azzaroni and Dr. Matías Rafti at SoftMatter Lab-INIFTA-UNLP with an scholarship granted by CONICET.

Dr Matías Rafti holds a Chemistry BSc from the National University of La Plata (Universidad Nacional de La Plata – 2003), and completed a PhD project on simulations and experiments for Heterogenous Catalysis under vacuum conditions, (2007, Prof. Vicente (Argentina, UNLP), and Prof. Imbihl (PCI, University of Hannover, Germany). He is currently a Staff Researcher at CONICET-Argentina and docent at the SoftMatter Lab-INIFTA-UNLP. Our current projects take advantage of both the synergy arising from close-collaboration with lab members with diverse expertise (e.g., x-ray scattering techniques, organic synthesis, electrochemistry, colloidal chemistry), and the wide range of available techniques allowing for a thorough physical and chemical characterization; in order to pursue the synthesis of MOF composite materials (either in colloidal suspensions or film configuration) with potential for applications in energy-related and sensing technologies.

Could you briefly explain the focus of your article to the non-specialist (in one or two sentences only) and why it is of current interest?
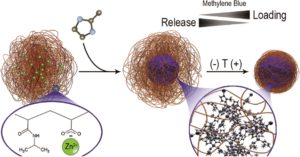
We aim to develop integrated materials (aka “composites”) using building blocks which would bring different features together; to combine such components in a robust composite while maintaining functionality is a non-trivial task. Taking advantage of the expertise developed in our lab covering aspects of polymer science (softmatter) and (somehow “harder”) porous polymers (Metal Organic Frameworks or MOFs); we developed a straightforward strategy which yields MOF@Polymeric_Microgel composites featuring stimuli-responsiveness (microgel) and enhanced surface area available for adsorption (MOF).
How big an impact could your results potentially have?
The novel strategy presented is very versatile, the Zn-based ZIF-8 MOF used as proof-of-concept could be easily replaced by other MOFs, which were already employed in many interesting applications beyond adsorption. Furthermore, the MOF/Microgel composition of such highly integrated composites can be controlled, thus opening the path to new design strategies towards stimuli-responsive adsorbants.
Could you explain the motivation behind this study?
This work was inspired by our experience working with stimuli responsive polymeric materials and the idea of conferring such an interesting platform with additional features. We had also been working recently in the synthesis of various MOFs for diverse uses (eg. adsorption); such materials are known to suffer from hydrolysis under mild/strong conditions in aqueous environments, and such drawback hinders the otherwise immense field of applications possible. The idea behind the reported work aimed to extend the scope of uses of polymeric microgels by endowing them with high surface area; and at the same, to provide additional stability for the embedded MOF phase, thus broadening the range of conditions suitable for adsorption in aqueous environments.
In your opinion, what are the key design considerations for your study?
Our study is based in a meticulous selection of the composition and chemical nature of the different players, and basic chemistry notions: by introducing moieties into the microgel’s network capable to precoordinate or preconcentrate the Zn cations, we have taken advantage of the well-known coordination chemistry to direct its heterogeneous nucleation and growth of the crystalline ZIF-8 inside the microgel.
Which part of the work towards this paper proved to be most challenging?
The strategy for integration of MOF and microgel phases into the composite involves the use of a pre-coordination stage, in which metal ions were adsorbed onto exposed carboxylate moieties for subsequent MOF grow within the polymeric phase. The two main challenges we faced in the present work can be summarized as follows; i) finding the appropriate concentration of pre-coordinated ionic metal precursors for MOF growth (which can be controlled by many parameters; e.g., the amount of carboxylate moieties exposed in the microgel, or the concentration of Zn2+ ions and exposure time during the preconcentration stage); and ii) finding the appropriate conditions for controlling the swelling state of the microgel which would be compatible with MOF growth (i.e., methanol content, and ionic strength).
What aspect of your work are you most excited about at the moment?
In our laboratory we continually look for opportunities to combine the know-how developed in different research areas explored by staff researchers. In particular, we are very excited about the many possibilities opened by the integration of MOFs, MOFs/Polymers and MOFs/biomolecules composites into electrochemical platforms with applications in energy storage/conversion and biosensing.
What is the next step? What work is planned?
Regarding the work related to the present article, the next evident step would be to extend the characterization of the synthetized composite and to explore its possibilities as adsorptive platform. Specifically to explore new ways to confer selectivity and to acquire further control on loading/release mechanism.
Synthesis and characterization of thermoresponsive ZIF-8@PNIPAm-co-MAA microgel composites with enhanced performance as an adsorption/release platform
Juan A. Allegretto, Juan M. Giussi, Sergio E. Moya, Omar Azzaroni and Matias Rafti
RSC Adv., 2020, 10, 2453-2461
DOI: 10.1039/C9RA09729E , Paper
 Submit to RSC Advances today! Check out our author guidelines for information on our article types or find out more about the advantages of publishing in a Royal Society of Chemistry journal.
Submit to RSC Advances today! Check out our author guidelines for information on our article types or find out more about the advantages of publishing in a Royal Society of Chemistry journal.
Keep up to date with our latest HOT articles, Reviews, Collections & more by following us on Twitter. You can also keep informed by signing up to our E-Alerts.