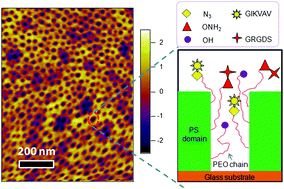
By precisely controlling the number of various adhesive ligands in integrin-sized nanodomains, this study provides important insights about the impact of local ligand redundancy on mesenchymal stem cell adhesion and phenotype.
In regenerative medicine, one of the limiting factors has been the number, complex isolation and limited lifespan of patients’ differentiated cell types for seeding scaffolds and subsequent cultivation of a functional tissue. The use of patient-specific stem cell populations, which have a prolonged life-span and can potentially be differentiated into any cell type desired, has emerged as the prevailing tissue engineering paradigm in the past decade. Despite its tremendous potential, steering stem cell differentiation towards a specific phenotypical outcome has been challenging. Polymer surfaces have been used extensively to elucidate the permissive cues required to drive selective differentiation, such as surface functionalities and adhesive molecules. Especially the impact of surface distribution and concentration of adhesive ligands remains a question mark. Yet, it is challenging to tether multiple distinct functionalities in a controllable manner and assess their respective effects on stem cell adhesion and differentiation.
Based at the University of Queensland, Justin Cooper-White and Haiqing Li sought to increase the understanding of surface ligand-dependent stem cell fate by precisely controlling the concentration and spatial organization of various ligands. To this end, they analyzed the effects of two well-known cell adhesion ligands, IKVAV and RGD, on mesenchymal stem cell adhesion and morphology.
Polystyrene-polyethyleneoxide (PS-PEO) block copolymers were shown to self-assemble into polymer films with a uniform distribution of cylindrical nanodomains of PEO, approximately the size of adhesion-controlling cell integrin pairs. By adding varying percentages of azide- or aminooxy-terminated PEO, orthogonal click chemistry was used to sequentially functionalize those cylindrical nanodomains with a controllable local density of grafted adhesion sequences IKVAV and RGD. Then, the researchers assessed the effects of varying local IKVAV and RGD densities in the nanodomains on human mesenchymal stem cell adhesion, spreading morphology and focal adhesion complex formation. They found that with increasing IKVAV or RGD ligand density, leading to ligand ‘redundancy’ for integrin pairs, stem cells showed increased attachment, spreading and stress fiber formation. Moreover, an increase in ratio between RGD and IKVAV densities increased stem cell adhesion.
Together, the researchers found that PS-PEO block co-polymers with functional end-groups, permitting orthogonal chemistry, allowed tight control of ligand decoration within cylindrical nanodomains. Furthermore, using IKVAV and RGD as exemplars, they showed the effect of varying ligand redundancy within nanodomains on stem cell fate. The reported self-assembling substrates offer a highly flexible platform technology to investigate and elucidate the impact of various ligands and their density on integrin binding, which also determines cell phenotype.
Changing ligand number and type within nanocylindrical domains through kinetically constrained self-assembly – impacts of ligand ‘redundancy’ on human mesenchymal stem cell adhesion and morphology
H. Li and J. J. Cooper-White
Biomater. Sci., 2014, Advance Article DOI: 10.1039/C4BM00109E
 Robert van Lith is currently a Ph.D. Candidate in the Biomedical Engineering department at Northwestern University, working on novel biomaterials to modulate oxidative stress in tissues. He received an American Heart Association Fellowship and Society for Biomaterials award for his work. He holds B.S. and M.S. degrees in Biomedical Engineering from Eindhoven University of Technology, the Netherlands. Read more about Robert’s research publications here.
Robert van Lith is currently a Ph.D. Candidate in the Biomedical Engineering department at Northwestern University, working on novel biomaterials to modulate oxidative stress in tissues. He received an American Heart Association Fellowship and Society for Biomaterials award for his work. He holds B.S. and M.S. degrees in Biomedical Engineering from Eindhoven University of Technology, the Netherlands. Read more about Robert’s research publications here.