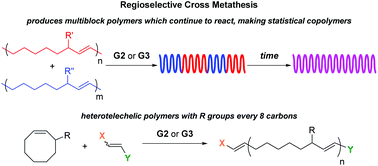
Radlauer et al. report the regioregularity of ring-opening metathesis polymerization and cross metathesis reactions for the synthesis of block and heterotelechelic materials.
Among the two distinct olefin metathesis polymerization methods, namely acyclic diene metathesis (ADMET) polymerization and ring opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP), ROMP possesses the advantage of proceeding by a chain growth mechanism and has been demonstrated to deliver polymers with an R substituent every 8 carbons from 3-substituted cyclooctene (3RCOE) monomers. Although secondary metathesis such as cross metathesis (CM) can occur between chains during ROMP, when the selectivity of 3RCOE monomers was examined, no studies on the CM were conducted. Towards this direction, Hillmyer and co-workers determined the CM of 3RCOE derivatives to be both regio- and stereoselective, making only a small fraction of t-TT and t-HH errors. As only a marginal increase in errors over time was observed, it was concluded that the system reached an equilibrium between the formation and fixing of errors. This stereo- and regioselectivity can be extended by combining polymers with different degrees of polymerization, or by combining polymers with different R substituents leading to the formation of multiblock or statistical copolymers depending on how long the CM is allowed to proceed. In the latter case, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) confirms the transition from two Tgs to one Tg corresponding to a multiblock and a statistical copolymer, respectively. Additionally, the location of end groups from an asymmetric chain transfer agent can be controlled, thus allowing access to predominantly heterotelechelic oligomers or polymers despite the CM reactions that can occur between the chains.
Tips/comments directly from the authors:
- In our experience if a polymer turned brown, it was generally caused by the presence of deactivated Grubbs catalyst. To remove this contaminant at the end of the polymerization, the polymer was dissolved in chloroform and stirred with carbon black. Subsequent filtration and reprecipitation of the polymer generally yielded clear and colorless materials.
- To obtain SEC data that was more easily interpreted, we used adjusted ratios of the polymers of different degrees of polymerization in the polymer-polymer cross metathesis experiments. Though the 1:1 scenario still showed immediate CM to an average N, the resolution between the two peaks was quite poor.
Any experiment involving the acetal-containing chain transfer agent required that each reaction component be filtered over basic alumina to avoid deprotection of the acetal moiety.
Read this exciting research for free until 25/11/2016 through a registered RSC account:
Regioselective cross metathesis for block and heterotelechelic polymer synthesis
M.R. Radlauer, M.E. Matta and M.A. Hillmyer,
Polym. Chem., 2016, 7, 6269-6278,
DOI: 10.1039/C6PY01231K
—————-
Dr. Athina Anastasaki is a web writer for Polymer Chemistry. She is currently an Elings fellow working alongside Professor Craig Hawker at the University of California, Santa Barbara (UCSB). Please visit this website for more information.