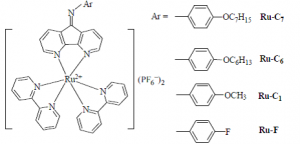
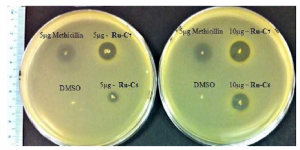
Posted on behalf of Jamie Humphrey, Editor
Our number one priority at Dalton Transactions is to ensure that the journal continues to support our community by providing excellent services for authors and by publishing only the best inorganic chemistry research. We strive to develop and innovate to make sure that the journal continues to serve the international inorganic community. This is very much at the heart of everything we do.

The truly international nature of the journal is represented not only in our authorship (we published articles from 70 countries in 2012), but also through the Editorial Board membership, including our team of Associate Editors – about half of the papers submitted to the journal are handled by this team, with the rest handled by the team of Editors based in Cambridge. Our Associate Editors span the globe, with editorial offices in the USA, UK, Germany, China and Japan. The Royal Society of Chemistry has also been developing its international staff presence in recent years and we now have editorial staff based in Japan, China and the USA, in addition to Royal Society of Chemistry offices in India, Africa and, more recently, Brazil.
In today’s information age, where we can sometimes feel overwhelmed with the amount of information that is available, access to reliable trustworthy knowledge has never been more important. At Dalton Transactions, our fair and impartial peer-review means the content we publish is always of the highest possible quality. Ensuring your research gets the right audience is also key. We have therefore introduced initiatives to lead to greater discoverability for articles published in the journal, and to develop additional measures of an article’s impact.
Dalton Transactions is part of a pilot programme between the Royal Society of Chemistry and Kudos, which aims to provide tools and services to help researchers maximise the usage and impact of their articles. The need for Kudos arises from developments in global academic and research policies that see evolving measures of ‘impact’ used to assess excellence. Kudos aims to provide a service to help researchers and their institutions measure, monitor and maximize the usage of and citations to their articles. The Royal Society of Chemistry also recently introduced a new system for monitoring article-level metrics in Dalton Transactions. The service collates online “mentions” of scholarly articles from social media, newspapers, blogs and other sources into a report that appears online with the article to showcase its uptake, visibility and societal impact. Article-level metrics represents a shift from measuring the impact of a journal to the impact of an article.
Supporting the community is at the heart of Dalton Transactions and is also at the core of the Royal Society of Chemistry, the world’s leading chemistry community. One way in which we supported chemists across the globe is through the funding of the International Year of Chemistry legacy grants. In 2012, over 60 of our member groups received grants each of £1000 to arrange events and activities to promote the chemical sciences. These had an international nature, and ranged from workshops for migrant children in Beijing and a science fair on water chemistry in southern India to supporting chemistry education in tsunami-affected areas in Sri Lanka. Learn more about these grants via www.rsc.org/scienceandtechnology/funding/iyclegacygrants.asp
Dalton Transactions continues to publish research from all areas of inorganic, organometallic and bioinorganic chemistry. Our Themed Issues bring together the best articles in topical research areas or highlight emerging subjects. Table 1 gives full details of the Themed Issues published in 2013.
Table 1 Dalton Transactions Themed Issues published in 2013
| Theme |
Guest Editor(s) |
|
| Coordination Programming: Science of Molecular Superstructures towards Chemical Devices |
Hiroshi Nishihara (Tsukuba University, Japan) and Hiroki Oshio (University of Tokyo, Japan) |
|
| |
| Molecular Precursors for Precision Synthesis of Nanomaterials |
Christophe Copéret and Maksym Kovalenko, ETH, Switzerland |
|
| |
| Vanadium in Inorganic Chemistry |
Debbie Crans, Colorado State University, USA and Craig McLauchlan, Illinois State University, USA |
|
| |
| Advances in Metal-Catalysed Polymerisation and Related Transformations |
Philip Mountford, University of Oxford, UK |
|
| |
| N-Heterocyclic Carbenes |
Catherine Cazin, St. Andrew’s University, UK |
|
| |
| Chemistry and Applications of Metal Complexes |
Maria Amélia Santos, University of Lisbon, Portugal |
|
| |
| Mechanistic Organometallic Chemistry |
Robert Crabtree, Yale University, USA |
|
| |
| Bioinorganic Chemistry |
Emma Raven, Leicester University, UK |
|
| |
| Boranes and Borohydrides |
Simon Aldridge, University of Oxford, UK |
|
Themed Issues planned for 2014 include Carboranes (Guest Editors: Professor Guo-Xin Jin, Fudan University, China and Professor Zuowei Xie, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong), Inorganic Chemistry for Renewable Energy Conversion and Storage (Guest Editor, Professor Lars Kloo, KTH, Sweden), Layered Inorganic Solids (Guest Editors: Professor Russell Morris, University of St. Andrews, UK, Dr Jiri Cejka, J. Heyrovsky Institute of Physical Chemistry, Hungary, Dr Petr Nachtigall, Charles University, Czech Republic, Dr Wieslaw Roth, Jagiellonian University of Krakow, Poland), New Talent: Europe (Guest Editors, Professor Dr Matthias Tamm, Technische Universität Braunschweig, Germany and Dr Marc D. Walter, Technische Universität Braunschweig, Germany), Organometallic and Coordination Derivatives of Nanocarbons (Guest Editors, Professor Andrei Khlobystov, University of Nottingham, UK and Professor Andreas Hirsch, University Erlangen-Nuremberg, Germany), New Expeditions in Polar Organometallic Chemistry (Guest Editor, Professor Eva Hevia, University of Strathclyde, UK), Spectroscopy of Inorganic Excited States (Guest Editor, Dr Julia Weinstein, University of Sheffield, UK) and Synergy between Experiment and Theory (Guest Editor, Professor Eric Clot, University of Montpellier, France).
2014 will be a busy year for inorganic chemistry conferences, and I hope that you will look out for me or Deputy Editor Fiona McKenzie – we would love to meet up with you! Two such meetings are the Dalton Discussions, which will take place in the UK. We are proud to publish the presented papers in Dalton Transactions. The titles of the 2014 meetings are ‘Advancing the Chemistry of the f-elements: Dalton Discussion 14’ (28–30 July 2014 Edinburgh, UK) and ‘Metal ions in medical imaging: optical, radiopharmaceutical and MRI contrast: Dalton Discussion 15’ (8–10 September 2014, York, UK). Another important inorganic meeting organised by the Royal Society of Chemistry in 2014 is the 13th ISACS meeting (Challenges in Inorganic and Materials Chemistry (ISACS13)) which will take place in Dublin, Ireland, 1–4 July 2014. To discover which conferences the Editorial Team will be attending in 2014, follow us on twitter (@DaltonTrans and @humphreyj).
We were pleased to support a number of international conferences in 2013 through sponsorship – you may even have attended one of our sponsored lectures. We give support to younger members of the community via poster prizes, and in 2013 we awarded 22 poster prizes, celebrating the achievements of members of our community in the early years of their academic careers. If you are organising a conference in 2014 and you would like us to sponsor a poster prize, please let us know.
With a thriving worldwide network, and a not-for-profit ethos, the Royal Society of Chemistry is the best place to publish work that advances excellence in the chemical sciences. Publish with Dalton Transactions and you’ll be supporting the wider scientific community and future generations of chemists and chemical scientists.
Have a fantastic 2014!
Download the PDF here

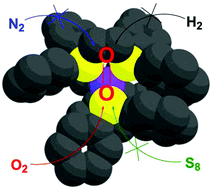
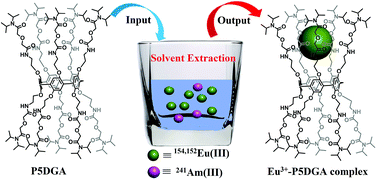








 Ian Mallov is currently a Ph.D. student in Professor Doug Stephan’s group at the University of Toronto. His research is focused on synthesizing new Lewis-acidic compounds active in Frustrated Lewis Pair chemistry. He grew up in Truro, Nova Scotia and graduated from Dalhousie University and the University of Ottawa, and worked in chemical analysis in industry for three years before returning to grad school.
Ian Mallov is currently a Ph.D. student in Professor Doug Stephan’s group at the University of Toronto. His research is focused on synthesizing new Lewis-acidic compounds active in Frustrated Lewis Pair chemistry. He grew up in Truro, Nova Scotia and graduated from Dalhousie University and the University of Ottawa, and worked in chemical analysis in industry for three years before returning to grad school.