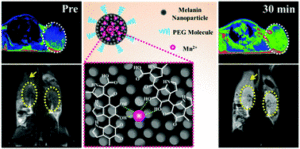
Good quality MRI contrast agents require profound tumor-targeting ability, well relaxivity, along with rapid clearance properties. In this context, endogenous biological mimicking biomaterials, with high biodegradability and biocompatibility hold enormous potential for the development of clinically translatable nanotheranostics platforms. Manganese plays a crucial role in mitochondrial and cellular function and recently, manganese (Mn)-based contrast agents have been receiving significant attention, due to improved biosafety and superior contrast abilities. However, the long term toxicity and non-biodegradability of these inorganic nanoplatforms have significantly halted their clinical progress. In contrast to this, melanin, an asymmetrical natural biopolymer, has garnered enormous attention due to good biocompatibility, biodegradability and MRI contrast imaging abilities. Hence, exploring endogenous natural materials with high contrast properties seems promising as clinically translatable in vivo MRI imaging contrast agent.
The Wang group developed an ultra small and water soluble Mn2+ chelating pegylated melanin nanoparticles (MNP-PEG-Mn) demonstrating excellent tumor-targeting Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) ability. The MNP-PEG-Mn nanoparticles show a size of 5.6 nm displaying high chelating stability and low cytotoxicity. Interestingly, the MNP-PEG-Mn nanoparticles show improved longitudinal relaxivity compared to clinically approved MRI contrast agent Gadodiamide. In vivo studies further showcased excellent tumor targeting abilities upon intravenous administration of MNP-PEG-Mn nanoparticles in mouse model. The author further showed that the MNP-PEG-Mn nanoparticles could be excreted via hepatobiliary and renal routes. In this process negligible toxicity was generated to body tissues that indicate high biocompatibility. Altogether, these results clinically validate the tumor targeted T1 MRI contrast properties of bio-mimicking melanin conjugated manganese nanoparticles.
Melanin-manganese nanoparticles with ultrahigh efficient clearance in vivo for tumor-targeting T1 magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent . Biomater. Sci., 2018, 6, 207-215.
This article is free to read until 28 February!
About the Web writer:
 Dr. Sudip Mukherjee is a Web Writer for Biomaterials Science. He is currently a Postdoctoral Research Associate working at the Department of Bioengineering at the Rice University. His research is involved in the development of advanced nanomaterials for drug/gene delivery in cancer theranostics, immunotherapy, immunomodulatory applications & angiogenesis. He published a total of ~30 research articles/patents. He serves as International Advisory Board Member for ‘Materials Research Express‘, IOP Sciences. He is an associate member (AMRSC) of The Royal Society of Chemistry, UK. He serves as reviewer for several international journals like Chem Comm, J Mater Chem A, J Mater Chem B, Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology, RSC Advances, IOP Nanotechnology etc. He can be contacted by email at sudip.mukherjee@rice.edu or on Twitter.
Dr. Sudip Mukherjee is a Web Writer for Biomaterials Science. He is currently a Postdoctoral Research Associate working at the Department of Bioengineering at the Rice University. His research is involved in the development of advanced nanomaterials for drug/gene delivery in cancer theranostics, immunotherapy, immunomodulatory applications & angiogenesis. He published a total of ~30 research articles/patents. He serves as International Advisory Board Member for ‘Materials Research Express‘, IOP Sciences. He is an associate member (AMRSC) of The Royal Society of Chemistry, UK. He serves as reviewer for several international journals like Chem Comm, J Mater Chem A, J Mater Chem B, Journal of Biomedical Nanotechnology, RSC Advances, IOP Nanotechnology etc. He can be contacted by email at sudip.mukherjee@rice.edu or on Twitter.